
We cloned the katB gene encoding one of the catalase-peroxidases, constructed lacZ fusion and null strains, and identified a role for katB in H 2O 2 resistance of the free-living organism and in infection of human macrophage lines. pneumophila contains two bifunctional catalase-peroxidases and no monofunctional catalases or peroxidases. pneumophila because in other bacterial species these genes have been extremely useful tools for studying the stationary-phase response. We began an investigation of catalase-peroxidases in L.

We showed that the stationary-phase viability of a katG null mutant in Caulobacter crescentus is reduced by 6 orders of magnitude compared to that of the wild type, which is indicative of the importance of that catalase-peroxidase in stationary-phase survival ( 32). coli katG, encoding a catalase-peroxidase, and xth, encoding the DNA repair enzyme exonuclease III, are other antioxidant enzymes that are expressed in the stationary phase under the control of RpoS, the stationary-phase sigma factor ( 14, 19, 21). The Escherichia coli KatE catalase is a hallmark of the stationary phase and is part of the cross-resistance to stress that accompanies starvation. In many bacterial species, genes controlling the antioxidant response play important roles in the stationary phase.

pneumophila may be tools for identifying genes in pathways leading to virulence. Therefore, genes in stationary-phase pathways of L. Stationary-phase gene expression has been associated with acquisition of virulence traits in other bacterial pathogens, e.g., Salmonella species, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Yersinia enterocolitica ( 2, 8, 18, 23). These observations led to the model where the stationary phase is a necessary prerequisite to the acquisition of virulence by legionella and not merely a stress state to be endured between rounds of intracellular multiplication ( 5). pneumophila virulence traits, including cytotoxicity, infectivity, and sodium sensitivity, are absent from exponentially growing cultures but are expressed in response to starvation. It has recently been shown that several L. pneumophila must survive starvation conditions between periods of replication in a suitable host. These epidemiological considerations indicate that L. pneumophila is most frequently aerosolized are nutrient sparse: showerheads, respirators, air conditioning ducts and water cooling towers ( 10, 29, 30). Legionella pneumophila is an intracellular parasite and the causative organism of Legionnaires’ pneumonia, a disease spread by aerosolization of the pathogen from environmental reservoirs. Analysis of the changes in katB expression and in the total catalase and peroxidase activity during growth indicates that the 8- to 10-fold induction of peroxidase activity that occurs in stationary phase is attributable to KatA, the second L. KatB is similar to the KatG catalase-peroxidase of Escherichia coli in its 20-fold induction during exponential growth and in playing a role in resistance to hydrogen peroxide. Null mutants in katB are delayed in the infection and lysis of cultured macrophage-like cell lines. The gene encoding the KatB catalase-peroxidase was cloned and sequenced, and lacZ fusion and null mutant strains were constructed. pneumophila was shown to contain two bifunctional catalase-peroxidases and to lack monofunctional catalase and peroxidase.
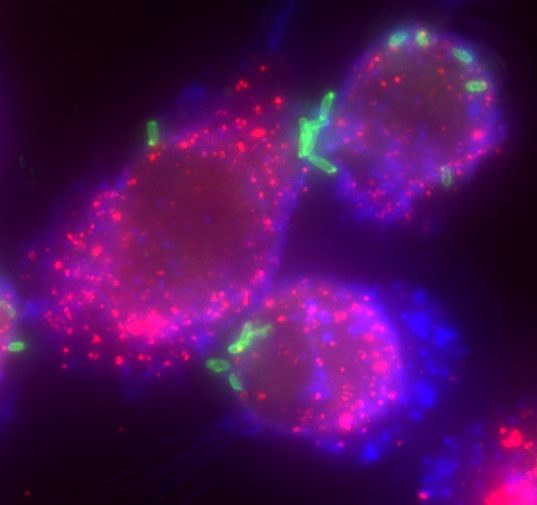
pneumophila, an investigation of these enzymes was initiated. Since catalase-peroxidases have been extremely useful markers of the stationary-phase response in many bacterial species and may be an avenue for identifying virulence genes in L. Exposure to starvation conditions is known to induce several virulence traits in L. Legionella pneumophila, the causative organism of Legionnaires’ pneumonia, is spread by aerosolization from man-made reservoirs, e.g., water cooling towers and air conditioning ducts, whose nutrient-poor conditions are conducive to entrance into stationary phase.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
